Athletes and coaches in gymnastics, tumbling, and acrobatic sports constantly seek ways to enhance training safety while maintaining effective skill development. A gymnastic belt serves as an essential piece of equipment that bridges the gap between learning new techniques and performing them with confidence. This specialized training tool provides crucial support during assisted skill training, allowing athletes to practice complex movements with reduced risk of injury while building the muscle memory necessary for independent execution.

The integration of safety equipment in gymnastics training has evolved significantly over the past decades. Modern coaching methodologies emphasize progressive skill development through controlled environments where athletes can push their boundaries without compromising their physical well-being. A gymnastic belt represents this philosophy perfectly by offering coaches and athletes a reliable method to practice advanced techniques under controlled conditions. The equipment enables proper body positioning and provides necessary support during critical phases of skill execution, making it an indispensable tool in professional training facilities worldwide.
Understanding Gymnastic Belt Functionality
Core Design Principles
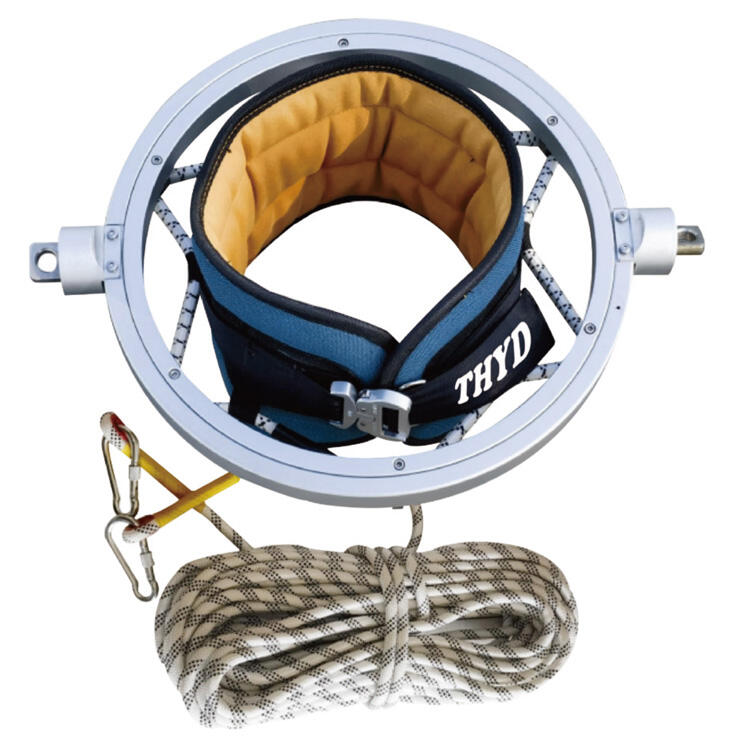
The fundamental design of a gymnastic belt centers around providing strategic support to an athlete's core and hip area during assisted training sessions. These belts typically feature reinforced stitching and durable materials capable of withstanding repeated stress from dynamic movements. The belt's construction includes padded sections that distribute pressure evenly across the athlete's torso, preventing uncomfortable pressure points that could distract from proper technique execution. Most quality gymnastic belt models incorporate adjustable strapping systems that accommodate athletes of various sizes while maintaining secure attachment points for safety lines or coaching assistance.
The ergonomic considerations in gymnastic belt design extend beyond basic comfort to encompass biomechanical efficiency. Engineers and sports equipment specialists collaborate to create belts that support natural body movement patterns while providing necessary external assistance. The positioning of attachment points on a gymnastic belt corresponds to the body's center of gravity, ensuring that applied forces enhance rather than interfere with proper technique development. This careful attention to anatomical alignment helps athletes maintain correct body positioning throughout assisted skill training sessions.
Material Specifications and Safety Standards
Professional-grade gymnastic belt construction utilizes high-tensile strength materials specifically selected for their durability and safety characteristics. The webbing materials undergo rigorous testing to ensure they can handle dynamic loads encountered during assisted training exercises. Safety certifications require gymnastic belt manufacturers to meet specific strength requirements, often exceeding normal operational loads by significant safety margins. These standards ensure that equipment failure remains virtually impossible under proper usage conditions.
Quality control processes for gymnastic belt production include multiple inspection stages where each component receives thorough evaluation. The stitching patterns, buckle mechanisms, and attachment hardware all undergo individual testing before assembly into complete units. This comprehensive quality assurance approach ensures that every gymnastic belt meets or exceeds established safety standards while providing reliable performance throughout its operational lifespan. Regular equipment inspections and maintenance protocols further enhance the safety profile of these essential training tools.
Safety Enhancement Mechanisms
Fall Prevention and Impact Reduction
The primary safety benefit of using a gymnastic belt during assisted training lies in its ability to prevent uncontrolled falls and reduce impact forces when mistakes occur. When athletes attempt new skills, the natural learning process includes failed attempts and incomplete rotations that could result in dangerous landings. A properly implemented gymnastic belt system allows coaches to provide immediate assistance, preventing athletes from falling to the ground or landing in compromising positions.
The impact reduction capabilities of gymnastic belt systems extend beyond preventing ground contact to managing the forces experienced by athletes during assisted catches or supported landings. When coaches utilize the belt to arrest an athlete's movement, the distributed load across the torso helps prevent localized stress concentrations that could cause injury. This controlled deceleration process allows athletes to experience the full range of motion associated with their intended skill while maintaining safety throughout the entire sequence.
Confidence Building Through Controlled Risk
Psychological safety represents another crucial aspect of gymnastic belt implementation in training programs. Athletes often face mental barriers when learning advanced skills, particularly those involving inverted positions or multiple rotations. The security provided by a gymnastic belt system helps athletes overcome fear-based limitations by offering tangible assurance that assistance is readily available if needed. This psychological support enables more aggressive skill attempts and faster progression through learning phases.
The confidence-building effects of gymnastic belt training create positive feedback loops that accelerate skill development. Athletes who feel secure during practice sessions demonstrate increased willingness to attempt challenging elements and maintain better focus on technique rather than safety concerns. This enhanced mental state translates to improved learning outcomes and more efficient training sessions. Coaches report that athletes using gymnastic belt assistance systems typically progress through skill progressions more rapidly than those relying solely on traditional spotting methods.
Training Applications Across Disciplines
Tumbling and Floor Exercise Integration
Tumbling training represents one of the most common applications for gymnastic belt systems, particularly during back handspring and back tuck development. The belt allows coaches to provide consistent support through critical phases of these skills while athletes develop the necessary strength and coordination for independent execution. During back handspring training, the gymnastic belt enables coaches to assist with proper shoulder positioning and timing without physically interfering with the athlete's natural movement patterns.
Advanced tumbling sequences benefit significantly from gymnastic belt integration, especially when athletes progress to multiple skill combinations. The belt system allows for seamless assistance throughout connected elements, helping athletes maintain proper rhythm and positioning between individual skills. This continuous support proves invaluable during layout and twisting skill development, where slight timing variations can result in dangerous landing scenarios without proper assistance.
Trampoline and Aerial Skill Development
Trampoline training environments utilize gymnastic belt systems extensively for teaching complex aerial maneuvers and multiple rotation skills. The three-dimensional nature of trampoline skills requires assistance systems capable of managing forces in multiple directions simultaneously. A gymnastic belt provides the necessary attachment points for overhead rigging systems that can support athletes through complete skill sequences while maintaining natural bounce characteristics.
The adjustable nature of modern gymnastic belt designs accommodates the varying support requirements associated with different aerial skills. Beginning athletes might require consistent assistance throughout entire rotations, while advanced practitioners need only minimal guidance during specific skill phases. The flexibility inherent in gymnastic belt systems allows coaches to customize assistance levels precisely, promoting optimal learning conditions for athletes at all skill levels.
Professional Implementation Strategies
Coach Training and Certification Requirements
Effective gymnastic belt implementation requires comprehensive coach education covering proper equipment usage, safety protocols, and progressive training methodologies. Professional coaching organizations typically mandate specific training modules addressing assisted training techniques and equipment safety standards. These educational requirements ensure that coaches understand both the capabilities and limitations of gymnastic belt systems before implementing them in their training programs.
The certification processes for gymnastic belt usage often include hands-on training components where coaches practice assistance techniques under supervised conditions. This practical experience helps coaches develop the timing and positioning skills necessary for effective belt implementation. Regular continuing education requirements ensure that coaches stay current with evolving best practices and safety recommendations as equipment technology and training methodologies advance.
Facility Setup and Safety Protocols
Proper facility configuration plays a crucial role in maximizing the safety benefits of gymnastic belt systems. Training areas must provide adequate clearance around equipment usage zones and maintain appropriate surface conditions for safe skill practice. Overhead rigging systems require professional installation and regular inspection to ensure structural integrity under operational loads. The gymnastic belt represents just one component of a comprehensive safety system that includes proper facility design and equipment maintenance protocols.
Safety protocol development for gymnastic belt usage encompasses equipment inspection procedures, athlete preparation requirements, and emergency response plans. Regular equipment inspections identify potential wear issues before they compromise safety, while standardized athlete preparation ensures consistent safety practices across all training sessions. Emergency procedures specifically address scenarios unique to assisted training environments, preparing coaches and athletes to respond appropriately to equipment malfunctions or unexpected situations during belt-assisted skill attempts.
Advanced Applications and Skill Progression
Complex Skill Integration
Elite-level training programs utilize gymnastic belt systems for developing highly complex skill combinations that would be impossible to practice safely through traditional spotting methods. These advanced applications often involve multiple coaches working coordinated assistance patterns to support athletes through extended skill sequences. The gymnastic belt serves as the central coordination point for these multi-person assistance systems, providing consistent athlete attachment while allowing coaches to manage different aspects of skill execution simultaneously.
The progression from basic skill development to complex combination training requires careful modification of gymnastic belt implementation strategies. Coaches must gradually reduce assistance levels while maintaining safety standards appropriate for increasingly difficult skill attempts. This progressive reduction process helps athletes develop confidence in their independent abilities while ensuring that safety support remains available during critical learning phases. Advanced training facilities often employ sophisticated pulley and counterweight systems that allow for precise assistance level adjustments throughout skill progressions.
Specialized Training Environments
Different training environments require specialized approaches to gymnastic belt implementation that account for unique facility characteristics and equipment configurations. Water-based training facilities utilize modified gymnastic belt systems designed to function effectively in aquatic environments, while foam pit installations require belt configurations that accommodate the unique landing characteristics of these safety surfaces. Each specialized environment demands specific safety considerations and equipment modifications to maintain optimal training conditions.
The adaptation of gymnastic belt systems to specialized training environments often involves collaboration between equipment manufacturers and facility designers to develop custom solutions. These specialized implementations maintain the core safety and training benefits of standard gymnastic belt systems while accommodating unique environmental requirements. The resulting equipment configurations provide coaches with versatile tools capable of supporting athlete development across diverse training scenarios and facility types.
FAQ
What age groups can safely use gymnastic belt training systems
Gymnastic belt systems are suitable for athletes of all ages, from young beginners to elite adult competitors. The key factor is proper sizing and appropriate skill-level application rather than age restrictions. Youth athletes typically benefit significantly from gymnastic belt training as it allows them to learn proper technique while building confidence in a controlled environment. Adult athletes returning to gymnastics or learning new skills also find gymnastic belt assistance valuable for overcoming fear barriers and reducing injury risk during skill acquisition phases.
How often should gymnastic belt equipment undergo safety inspections
Professional training facilities should conduct daily visual inspections of gymnastic belt equipment before each use session, checking for obvious wear, damage, or hardware malfunctions. Comprehensive monthly inspections should examine stitching integrity, buckle function, and material condition more thoroughly. Annual professional inspections by qualified equipment specialists ensure that subtle wear patterns or structural issues receive proper evaluation. Any gymnastic belt showing signs of excessive wear or damage should be immediately removed from service until professional repair or replacement occurs.
Can gymnastic belt training replace traditional manual spotting techniques
Gymnastic belt systems complement rather than replace traditional spotting methods, offering unique advantages in specific training situations. Manual spotting remains essential for teaching proper body positioning and providing tactile feedback during initial skill learning phases. The gymnastic belt excels in situations requiring sustained assistance through complete skill sequences or when practicing skills that would be difficult or dangerous to spot manually. Most effective training programs combine both approaches, using gymnastic belt assistance during appropriate skill development phases while maintaining manual spotting for technique refinement and initial skill introduction.
What maintenance procedures extend gymnastic belt lifespan
Proper storage in clean, dry environments prevents accelerated material degradation and maintains gymnastic belt integrity over extended periods. Regular cleaning with mild soap and water removes chalk, sweat, and other contaminants that can compromise material properties. Avoiding exposure to sharp objects, extreme temperatures, and chemical cleaners helps preserve the structural integrity of gymnastic belt components. Rotating multiple belts through regular use prevents excessive wear on individual units while ensuring backup equipment availability during peak training periods.